Use session keys
Session keys are programmable access tokens with specific permissions, designed for controlled interactions. Examples include:
- Granting access to specific areas or features
- Limiting usage to a set amount of resources (for example, 1000 units of currency)
- Time-bound validity (for example, expiring after three days)
Permissions can be combined, enabling fine-tuned, context-specific capabilities.
This section guides you through registering a session key and using it to mint an asset with a user's smart account. Choose your preferred implementation approach:
Standard (EIP-1193 provider)
Using EIP-7715. The request method of the EIP-1193 provider can be used to request signatures. First, get the provider:
import openfort from "./openfortConfig"
// This example assumes you have already checked that Openfort 'embeddedState' is
// `ready` and the user is `authenticated`
const provider = await openfort.embeddedWallet.getEthereumProvider();Smart wallets support sending a batch of transactions in a single, atomic submission to the network.
To register a session key with a smart wallet, call the wallet_grantPermissions method.
As an example, you might batch together a transaction to approve a USDC spender and to transfer USDC like so:
import { generatePrivateKey, privateKeyToAccount } from 'viem/accounts';
const sessionKey = generatePrivateKey();
const accountSession = privateKeyToAccount(sessionKey).address;
await provider.request({
method: 'wallet_grantPermissions',
params: [
{
signer:{
type: "account",
data:{
id: accountSession
}
},
expiry: 60 * 60 * 24,
permissions: [
{
type: 'contract-call',
data: {
address: '0x2522f4fc9af2e1954a3d13f7a5b2683a00a4543a',
calls: []
},
policies: []
}
],
},
],
});Integration with wallet libraries
Popular libraries provide convenient methods for registering session keys:
| Library | Method |
|---|---|
| Viem | Use the wallet_grantPermissions action |
Openfort SDK method
1. Create a session key Client side
After you authenticate your user with your regular authentication system, you can create a session key for them. To create a session key, generate a key pair on the client side and send the address computed from the public key to your server.
Using one of the official Openfort client libraries, everything is handled for you.
- Install the client-side library:
- Initialize Openfort and create a session key:
// Set your public key. Remember to switch to your live PUBLIC key in production.
// See your keys here: https://dashboard.openfort.io/api-keys
import { Openfort } from '@openfort/openfort-js';
const openfort = new Openfort({
baseConfiguration: {
publishableKey: "YOUR_OPENFORT_PUBLISHABLE_KEY"
}
});1. Create a session key Server side
Viem create session key
import { generatePrivateKey, privateKeyToAccount } from 'viem/accounts';
const sessionKey = generatePrivateKey();
const accountSession = privateKeyToAccount(sessionKey).address;Ethers create session key
Using ethers, you can create a key pair on the server side of your application.
const sessionKey = ethers.Wallet.createRandom();The parameter sessionKey contains the address that you need to register.
After creating the session key, you can go ahead and register it.
2. Register a session key Server side Client side
To register a session key, first send the address from the session key to your server. You can get the address from the session key object created above like this:
const address = sessionKey.address;Then, from your server, make a request to the Openfort API or use one of our server libraries to register the session key.
Install Openfort on your server and initialize it with your secret key.
npm install @openfort/openfort-nodeInitialize with your secret key:
import Openfort from '@openfort/openfort-node'
const openfort = new Openfort('sk_test_...');The created session key would be valid since the 25th of May 2023 at 7
GMT (timestamp1685001000) and last for 1 hour (timestamp 1685001000).
For a useful resource to calculate timestamps online, visit UNIX Timestamp.Also, note how a policy indicates the policy that sponsors the gas fees of the transaction to register the session key.
Register the session key using Openfort:
curl https://api.openfort.io/v1/sessions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_SECRET_KEY" \
-d address="0x76e6...9341" \
-d chainId=80002 \
-d validUntil=1685004600 \
-d validAfter=0 \
-d account="acc_..." \
-d policy=pol_...3. Authorize the session key Client side
The owner of the account needs to authorize the new session key.
To do so, sign the signableHash from the nextAction object returned by the API call to register the session key.
"nextAction": {
"type": "sign_with_wallet",
"payload": {
"signableHash": "0x91b4efe3648c79467f7b50aa9bb1b4eae383a52dd6d741d39ece29ed2ef8362d"
}
},Once signed by the owner signer of the account,
send it to Openfort using the endpoint /v1/sessions/:id/signature as shown below:
curl https://api.openfort.io/v1/sessions/ses_.../signature \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_PUBLISHABLE_KEY" \
-d signature="xyz..."After registering the session key, you can see it in the dashboard under the user's page.
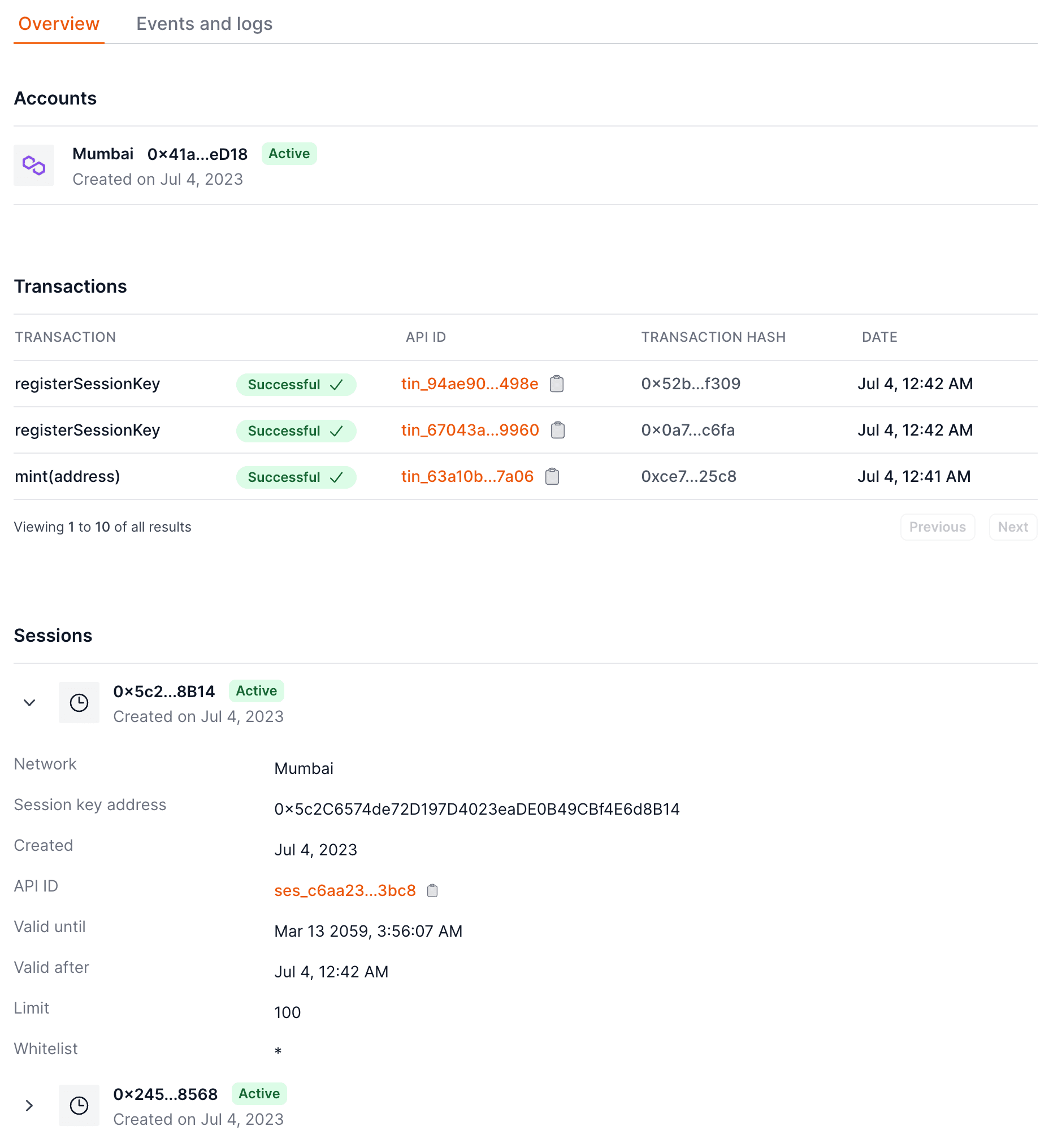
4. Use the session key Server side Client side
After the session key is registered, it can be used to authenticate requests from the player. Whenever you create a transaction intent from your backend, a signature is needed from the session key or owner of the users' smart account.
Create a transaction intent:
curl https://api.openfort.io/v1/transaction_intents \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_SECRET_KEY" \
-d account="acc_..." \
-d address="0x76e6...9341" \
-d chainId=80002 \
-d policy=pol_...After creating the transaction intent, the session key needs to sign the nextAction signableHash and send it to Openfort.
The response of the call to transaction intents contains a nextAction object like this:
"nextAction": {
"type": "sign_with_wallet",
"payload": {
"signableHash": "0x91b4efe3648c79467f7b50aa9bb1b4eae383a52dd6d741d39ece29ed2ef8362d"
}
},This signableHash needs to be signed by the session key like so:
Viem session signing example
import { generatePrivateKey, privateKeyToAccount } from 'viem/accounts';
const sessionKey = '0x...'; // The private key of the session key
const accountSession = privateKeyToAccount(sessionKey).
const signature = accountSession.signMessage({message: {raw: signableHash}});5. Revoke a session key Client side Server side
The owner of the account can always revoke the session key.
To do so, sign the signableHash from the nextAction object returned by the API call to revoke the session key.
curl https://api.openfort.io/v1/sessions/revoke \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_SECRET_KEY" \
-d account=acc_... \
-d address="0x76e6...9341" \
-d chainId=80002 \
-d policy=pol_...Make sure to sign the signableHash with the owner account and send it to Openfort using the endpoint /v1/sessions/:id/signature.

